The protection of personal data is as sensitive an issue as the rights and guarantees it contains. In the digital age, users are forced to give up identifying data every day, for the use of any program, tool, platform and some mobile applications.
In May 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GRDP) will come into force on the 25th of the month.
I’m sure you’re aware of regulations by now. It aims to protect the privacyof citizens’ personal data within the European Union by requiring greater accountability from those who, for various reasons, must collect data from them.
It also gives users the right to know what is being done with their data, for what purpose it is being collected and the right to unsubscribe, or request that it be deleted.
It should be noted that in the same week, Mark Zuckerbergtestified before the European Parliament, in the case of data leaks from Cambridge Analytica. As a measure, the founder of Facebook blocked the applications involved and other apps are being investigated.
The penalties for non-compliance are very high. For example, anyone who has personal data without the express consent of the data subject may be fined up to 20 million euros or 4% of the total annual turnover of the business in the previous year.
The data protection rights provided for in the RGPD
Before going further into the subject of this regulation for mobile applications, the rights it establishes are listed below:
- To be informed: about the processing of data.
- Access by the data subject: to the processing of data, what, how, where and for what purpose they will be collected.
- The rectification or deletion of personal data or the limitation of such data. Even the right to oppose such treatment.
- Portability: you can always receive and dispose of your data.
- Not to submit to automated decision making, including profiling.
- To lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority.
RGPD-compliant data protection in mobile applications
As you can see, nothing escapes the RGPD. These regulations are protective. In addition, it is no secret to anyone, the countless data and information that can be collected from mobile devices, either because it is required (eg. health applications) or to improve the user experience and provide better services.
Both developers and publishers should bear in mind, from the design of the app and its marketing, the different features to be considered, on the processing and collection of data. It is essential to safeguard privacy, and to know and avoid risks that could violate security.
Besides the developers and the user, there are also other players: the application markets (Google Play, App Store, and others); the operating system of the Smartphone; the mobile phone manufacturers and third parties (advertising, cookies, banners, among others).
Between the mobile application and all these participants, there are some concepts you need to be familiar with in order to understand these rules a little more.
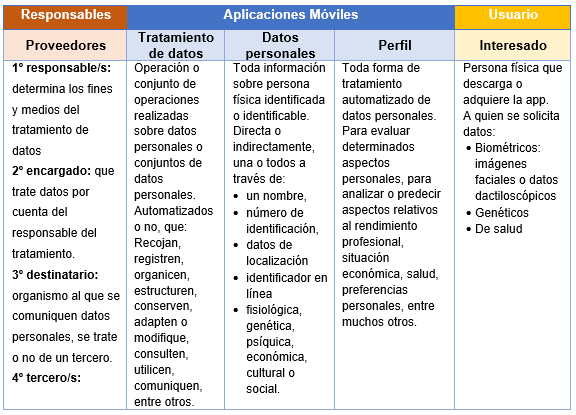
As you can see, mobile phones, and especially apps, collect a range of personal data, such as email, bank, contacts, location and other identifiers. So, as a developer or editor, you need to make sure that you indicate what data you are processing and where you will be storing it, without using your own mobile device or through a third party.
Key aspects for data processing in mobile applications
Now, here are some aspects to take into account, from the design of the app and in all your strategies, so that you can comply with the regulations, and you can develop your business offering security to users.
- Secure design: take care that you cannot force access to your app, or steal data, nor can the server where the app is hosted.
- Minimalist: uses little data, only what is necessary. Avoid unnecessary details.
- Consent: You must obtain consent before collecting any personal information. Inform at all times about the use you will make of it (treatment).
- Encryption: Encrypting user information collected.
- Informing users of securityincidents.
- Responds to requests: and especially if they relate to the above rights.
- Keep your application up to date.
This new law is a challenge. Both on the part of suppliers and users, as the practices recently employed throughout the commercial and digital sector were mostly contrary to the provisions of the RGPD.
Finally, one of the keys to this rule is consent. This must be free, specific, informed and unequivocal when processing personal data.
Follow us online and keep up to date on this and other mobile application or app topics.

